Conversational user interfaces (UI) that leverage natural language processing are revolutionizing how humans interact with technology. Also known as conversational AI, chatbots, or voice assistants, these interfaces aim to provide frictionless experiences by enabling users to communicate with systems conversationally using natural language.
In this comprehensive guide, we‘ll explore the world of conversational UI, including its history, key benefits, design best practices, real-world examples, and predictions for the future.
A Brief History of Conversational UI
The idea of conversational interfaces dates back to the 1960s when Joseph Weizenbaum created ELIZA, an early natural language processing system that mimicked conversation. However, conversational AI really took off in the 2010s with the rise of chatbots and voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant.
Advancements in natural language processing, neural networks, and AI have enabled rapid progress, making conversational interfaces more flexible, intelligent, and human-like. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated adoption as businesses looked for contactless customer service solutions.
Conversational UI is still evolving but has already become a preferred way for humans to interact with technology in the digital age. In fact, Gartner predicts that by 2025, 50% of enterprise interactions will happen through some kind of conversational interface.
Defining Conversational UI
But what exactly are conversational UIs?
Conversational user interfaces allow users to interact with applications conversationally using natural language (either text or voice). The system can understand requests, ask clarifying questions, and provide intelligent responses or perform actions through dialogue.
At a high level, there are two primary types:
- Text-based: Users interact by typing text queries and responses on platforms like chatbots, messaging apps, websites, etc.
- Voice-based: Users engage through spoken conversation with smart assistants like Siri, Alexa or Google Assistant.
In both cases, the goal is to provide an intuitive, frictionless user experience by mimicking human-like conversation.
Unlike traditional rigid graphical user interfaces (GUIs), conversational UIs adapt to users and leverage context to deliver personalized, natural interactions. The AI behind the scenes aims to understand each user‘s intent based on natural language processing and machine learning algorithms.
The Many Benefits of Conversational Interfaces
There are several key benefits driving adoption of conversational UI:
-
24/7 availability – Chatbots and voice assistants enable businesses to offer round-the-clock support without human agents. This improves customer satisfaction and reduces labor costs. According to Salesforce research, 73% of customers want support on weekends and evenings.
-
Natural interactions – Conversational UI provides a natural way for humans to communicate. Users don‘t have to learn complex menu structures or commands.
-
Multi-channel – These interfaces work across devices and platforms from mobile apps, websites, smart speakers and more. Over 70% of people use more than one messaging app.
-
Scalability – Chatbots and voice assistants can support millions of users simultaneously with minimal overhead, allowing massive scalability. WhatsApp alone sees over 65 billion messages sent per day.
-
Personalization – With access to user data and conversation history, conversational AI can offer personalized interactions. Over 80% of consumers are more likely to do business with a company if it offers personalized experiences.
-
Efficiency – By automating common requests, conversational AI saves time and effort for users. 30% of customer service organizations have seen over 50% reduction in call volume from conversational AI.
Key User Experience Principles
While the benefits are substantial, designing a good conversational interface is challenging. Here are some key UX principles:
- Clear onboarding – Guide users on capabilities upfront to set proper expectations.
- Context retention – Reference conversation history and user attributes to personalize dialog.
- Natural language – Allow free-form input without rigid menus or commands.
- Helpful error handling – Provide guidance when the user makes an unclear request.
- Concise responses – Be brief and to the point to mimic natural conversation.
- Consistency – Use recognizable phrases and patterns.
Adhering to these principles creates smoother, "human" conversational flows.
Advanced Capabilities
With continuous advancements in natural language processing (NLP), conversational AI can handle increasingly sophisticated capabilities like:
- Complex query understanding
- Contextual recommendation engines
- Transactional abilities (e.g. placing an order)
- Question answering with knowledge graphs
- User intent prediction and profiling
- Dialog management and multi-turn conversations
- Integration with back-end systems and data
As the technology improves, the use cases for conversational UI expand.
Conversational UI Classifications
Conversational interfaces can be categorized into a few primary types:
Chatbots
Text-based chatbots allow users to interact conversationally via text through a chat interface. They often use dialog boxes or messaging platforms:
Chatbots rely heavily on natural language processing to understand text queries. They have become a popular way for brands to interact conversationally with customers for customer service, marketing, and other use cases.
According to Grand View Research, the global chatbot market size is expected to reach $107 billion by 2028, growing at a 24% annual rate.
Voice Assistants
Voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant allow hands-free, voice-driven interactions. The system understands speech input and responds back conversationally via audio.
While less sophisticated than chatbots in some ways, voice UIs provide an easy hands-free experience that can be helpful for activities like driving, cooking, or when screens are limited.
By 2025, it‘s projected there will be 8.4 billion voice assistants in use worldwide.
Avatars
Some conversational UIs utilize visual avatars that users "talk" to conversationally. They aim to make interactions more natural through:
- Facial expressions
- Body language
- Visual cues
- Lip synchronization
Avatars create a more immersive, human-like conversational experience. However, they are less common due to technical complexity.
Hybrid Interfaces
Many conversational systems actually combine multiple interaction modes together into "hybrid" interfaces for greater flexibility.
For example, a bot could offer:
- Chatbot for text conversations
- Voice assistant for hands-free voice commands
- Visual avatar for video chats
By supporting multiple interaction modes, hybrid conversational UIs remove limitations of any single approach. Users have enhanced options for conversing naturally.
Best Practices for Conversational UI Design
Creating a useful, seamless conversational interface requires thoughtful design. Here are some best practices:
Limit scope
Don‘t attempt to create a conversational UI that can handle every customer query imaginable. Limit scope to a few key use cases and do them very well.
Overly broad bots quickly frustrate users. Make intent and capabilities clear upfront.
Provide clear cues
Ensure users understand what your conversational UI can and can‘t do through clear cues like greetings, menus, and documentation.
Set proper expectations on functions to avoid confusion down the line.
Leverage conversation history
Use context from prior interactions to personalize each conversation. Referencing past exchanges makes dialog more natural and human-like.
Plan responses carefully
Craft bot responses to guide users positively. Re-prompt clarifying questions if users provide unclear input rather than just saying "I don‘t understand."
Enable mixed initiation
Allow users to initiate interaction, but have the bot proactively reach out when appropriate as well. This makes conversations more natural.
Incorporate multimedia
Include images, videos, audio clips, and other media in responses when relevant to enrich interactions.
Test extensively with users
Continuously test and refine the conversational UI with real users during development. Their feedback reveals pain points and opportunities to improve.
Benchmark performance
Monitor metrics like conversation accuracy, containment rate, sentiment, and churn to benchmark performance. Set goals for improvement.
Continuously improve
Leverage logs, transcripts, and user feedback to provide ongoing training data for your NLP models. Continuously deploy improvements.
Top Conversational UI Examples and Case Studies
Let‘s look at some real-world examples of impactful conversational UIs across industries:
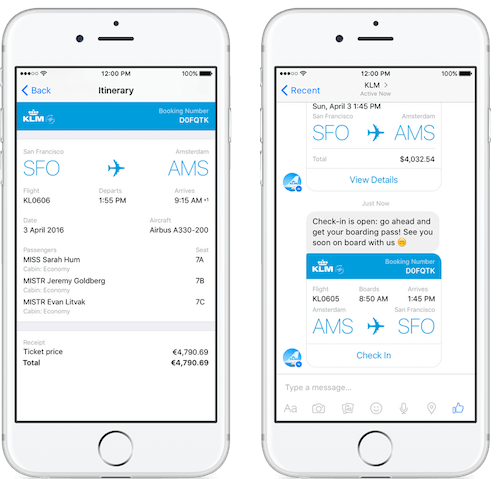
KLM Royal Dutch Airlines
One of the earliest airline chatbots, KLM launched its conversational app in 2016 for common flight-related tasks:
The virtual assistant enables passengers to:
- Check-in
- Select seats
- Order meals
- Get flight status
- Receive boarding passes
KLM‘s chatbot exemplifies key principles of good conversational design, providing a seamless personalized travel experience.
Woolworths Supermarkets
The Australian grocery chain deployed chatbots and voice assistants across their mobile app, website, and physical stores to assist shoppers:
The conversational interfaces handle customer queries on:
- Weekly specials and deals * Product information
- Recipes
- Store departments
- Payment issues
They also enable shop-from-home capabilities, driving greater customer engagement.
NHS
Britain‘s National Health Service developed a conversational tool to help users quickly navigate to appropriate medical services.
Users describe symptoms and the tool asks clarifying questions before pointing them to the right care options. Since launching, it has successfully directed over 1.3 million people to the resources they need.
Salesforce
The CRM giant acquired Conversica which uses conversational AI sales assistants to engage leads:
The bots have complex dialog capabilities to qualify prospects and surface sales opportunities via natural, personalized conversations at scale.
Sephora
Sephora‘s conversational commerce experience combines chatbots, voice shopping, and visualization to enable makeup recommendations:
Using AI, the bot gets to know each customer and makes personalized product suggestions based on their needs. This drives greater engagement and purchasing.
The Future of Conversational UI
While conversational interfaces have matured tremendously, there are still major innovations on the horizon:
Multimodal experiences
Leading conversational UIs are becoming multimodal, combining chat, voice, AR, and more for flexible interactions.
Emotion detection
Systems capable of detecting human emotion through verbal cues, facial expressions and more will enable greater empathy.
Generative AI
Powerful large language models like GPT-3 point to more fluent, coherent dialog capabilities for conversational AI.
Deployment acceleration
As development gets easier, conversational interface adoption will accelerate across industries.
Deeper personalization
With more customer data, businesses can deliver hyper-personalized conversations and recommendations.
Tighter IoT integration
Connecting conversational AI with Internet of Things devices will enable smarter homes, cars, and cities.
Immersive realities
Conversational UIs will provide natural control mechanisms for augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality.
Key Takeaways
Here are the critical lessons on conversational user interfaces:
- Conversational AI enables natural, frictionless interactions through voice and text. Adoption is accelerating.
- Thoughtful design focused on user needs is crucial to drive engagement over frustration.
- Leading implementations highlight the power of conversational UIs to improve customer experiences.
- Emerging innovations in emotion detection, generative AI, and mixed reality will continue enhancing these interfaces.
In our technology-driven world, conversational user experiences represent the next era of human-computer interaction. Companies that leverage conversational AI effectively will have a major competitive advantage in engaging digitally-savvy consumers moving forward.