Blockchain technology has rapidly gone from a niche concept to one of the most transformational innovations of our time. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of blockchain, its key benefits for business, and how it is likely to develop in 2024 and beyond.
What is Blockchain and How Does it Work?
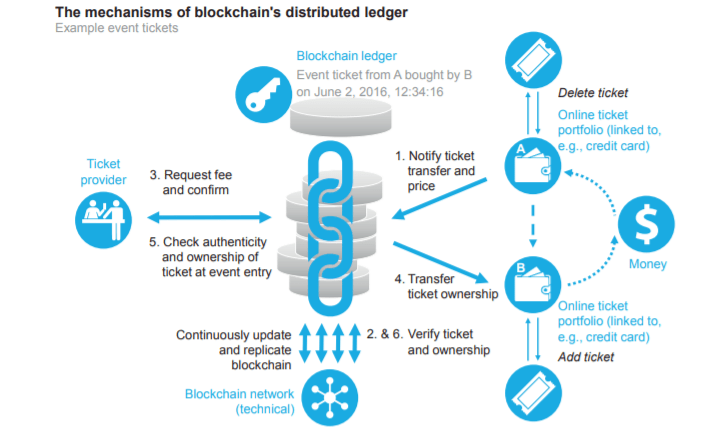
A blockchain is a distributed digital ledger that records transactions in blocks that are then cryptographically linked together in an immutable, chronological chain.
Here is a quick summary of how a blockchain network functions:
-
A transaction is initiated by a participant who broadcasts it to a peer-to-peer network consisting of computers known as nodes.
-
The network of nodes validates the transaction using algorithms to ensure it is authentic.
-
Once verified, the transaction is combined with others to create a new block of data.
-
The new block is given a unique cryptographic hash. This hash is linked to the previous block‘s hash, chaining them together.
-
The updated blockchain is simultaneously copied across the entire network of nodes to ensure transparency.
-
This decentralized structure means no single entity controls the data, providing security and trust.
Source: McKinsey
Some key principles of blockchain include:
-
Decentralization – Eliminates centralized control over data
-
Transparency – All participants can view the blocks and transactions
-
Immutability – Records cannot be altered retroactively due to cryptographic linking
-
Consensus – Transactions must be verified by majority of nodes to be approved
-
Automation – Smart contracts execute business terms without third parties
This unique architecture enables blockchain networks to offer enhanced security, transparency, automation, speed, and efficiency across many business sectors.
Key Business Benefits of Blockchain Technology
Here are some of the major ways blockchain delivers value for organizations:
Enhanced Security
- Encryption, timestamping, and immutable data make blockchain networks highly secure. This helps prevent fraud, hacking, and tampering.
- A 2021 survey found 55% of senior IT leaders considered security a top benefit of blockchain technology. [1]
Operational Efficiencies
- By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain streamlines processes and reduces transaction fees and costs.
- According to Accenture, blockchain could reduce bank infrastructure costs related to cross-border payments, KYC, and regulatory reporting by 70-80%. [2]
Faster Settlement
- Verification and confirmation of transactions on blockchain networks is near instantaneous. This accelerates settlement times from days to minutes.
- The DTCC estimates distributed ledger technology could reduce settlement times for some credit default swaps from 20-30 days to 1-2 days. [3]
Enhanced Traceability
- The immutable audit trail available via blockchain enables tracking movement of assets throughout the supply chain in detail.
- In foods, blockchain can help quickly trace sources of contamination, a process that typically takes weeks.
New Business Models
- Blockchain enables innovative capabilities such as cryptocurrencies, decentralized finance, tokenized assets, and autonomous organizations.
- The total market cap of DeFi applications reached $247 billion in March 2022, up from just $700 million in 2019. [4]
Improved Customer Experiences
- Transparent transaction histories foster trust and accountability between businesses and consumers.
- Blockchain-based loyalty programs allow consumers to securely manage points across multiple retailers.
Automated Processes
- Smart contracts enable complex business rules and integrated workflows to be defined, executed, and enforced automatically without third party involvement. This reduces costs and risk.
- According to Deloitte, manual processes comprise over 40% of total operational expenses at banks. Many of these could potentially be automated via smart contracts. [5]
The predicted global value of blockchain in 2025 and 2030 according to PwC:
| Year | Predicted Value |
|---|---|
| 2025 | $1.9 trillion |
| 2030 | $5.1 trillion |
Source: PwC [6]
As these figures indicate, blockchain adoption is accelerating rapidly.
Industries Making Use of Blockchain Technology
Many sectors are already exploring and implementing blockchain-based solutions:
Financial Services
- Payments infrastructure, trade finance platforms, clearing and settlement systems
- Cryptocurrencies, stablecoins, decentralized finance (DeFi)
Supply Chain & Logistics
- Tracking of goods, visibility of inventory across multiple parties, prevention of counterfeits
- Walmart uses blockchain for food supply chains, increasing traceability from 7 days to 2.2 seconds. [7]
Healthcare
- Secure healthcare record systems, transparent claims adjudication, connected medical devices
- Healthcare blockchain market projected to reach $1.7 billion by 2026. [8]
Government
- Identity verification, voting systems, benefits administration, documentation
- Dubai plans to use blockchain for 100% of government transactions by 2020. [9]
Energy
- Trading clean energy credits, e-mobility and EV charging, transparency across grids
- LO3 Energy operates blockchain-based microgrids in Brooklyn and expanding globally. [10]
Real Estate
- Property transactions, titling and deeds management, digital securities
- The tokenized real estate market is predicted to reach $1.4 billion by 2026. [11]
Public vs. Private vs. Permissioned Blockchains
There are several types of blockchain networks:
Public Blockchains
- Open, permissionless ledgers that anyone can join or access. Transactions are viewable to all participants.
- Uses include cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Benefits are full transparency and decentralization but has scalability and privacy limitations currently.
Private Blockchains
- Also known as enterprise or permissioned ledgers with controlled access and managed by a central entity.
- Restricted visibility improves privacy and enables faster processing.
- Used internally within organizations.
Permissioned Blockchains
- Hybrid model that combines aspects of public and private.
- Network is viewable to all but only authorized nodes can participate in consensus process.
- Enables collaboration between enterprises while retaining some control.
The choice depends on specific requirements around openness, privacy, speed, control, and governance needed.
Addressing Key Challenges and Limitations
Blockchain still faces some hurdles hindering mainstream enterprise adoption:
Scalability
- Public blockchains can only process 10 to 100 transactions per second, lagging traditional payment rails significantly.
- However, new solutions like sharding, sidechains, off-chain processing are addressing this.
Interoperability
- Networks today are often disconnected from each other. But polkadot, Cosmos and other "Layer 0" protocols aim to enable communication between chains.
Data Privacy
- While encryption protects data in transit and at rest, analytics often require access to decrypted data. Emerging techniques like zero-knowledge proofs aim to overcome this.
Energy Consumption
- Proof-of-work consensus used by Bitcoin and Ethereum is energy intensive. But newer protocols like proof-of-stake, proof-of-authority drastically reduce energy needs.
Talent Shortage
- As a newer technology, there is a lack of skilled blockchain developers. But training programs at institutions like UC Berkeley are helping close the gap.
Regulatory Uncertainty
- Laws around cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications are still evolving in most countries. But clear frameworks will likely emerge as the technology matures.
In coming years, many of these limitations are expected to lessen through advances in R&D, standards evolution, and regulatory clarity.
Developing a Blockchain Strategy
For enterprises exploring blockchain adoption, here are some recommendations:
Start Small
- Begin with a minimal viable product for one specific use case. Learn and improve before expanding scope.
Assess Technical Needs
- Factor in all requirements early – latency, throughput, privacy, storage, interfaces etc. This drives architecture choices.
Choose Developer Partners Carefully
- Find experts with proven skills in cryptographic implementations, consensus protocols, wallets, and interfaces.
Align to Long Term Roadmap
- Ensure initial blockchain project aligns to the broader digital transformation strategy and future needs.
Integrate with Existing Systems
- Plan for integration of blockchain network with core business applications, data stores, APIs and reporting tools.
Build with Future Scale in Mind
- Architect network and choose infrastructure to handle estimated transaction volumes, data storage, and user growth.
Extensively Test Prior to Launch
- Conduct security audits, functionality testing, and network load testing before deploying blockchain into production environments.
Emerging Trends and Applications to Watch
Here are some cutting edge blockchain use cases and developments gaining momentum:
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) – Algorithmic financial services built using public blockchain networks and open source software.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) – Unique blockchain-based tokens for digital art, collectibles, assets, and commodities.
Tokenized Securities – Traditional securities like stocks and bonds digitally represented on blockchains to enable fractional ownership and secondary trading.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) – Member-owned communities and organizations that operate on rules encoded transparently on blockchain.
Blockchain-Based Identity – Secure digital identities for people, devices, and entities to prevent fraud in online transactions and services.
Supply Chain Optimization – Granular tracking of items via blockchain to prevent counterfeits, ensure authenticity, and improve logistics.
Blockchain Access Management – Secure credentialing, authentication, and identity management powered by blockchain.
The blockchain ecosystem is advancing rapidly through a combination of technology innovation, standards evolution, business model transformation, and ecosystem collaboration.
The Future is Bright for Blockchain
Blockchain has graduated from hype to realization as enterprises move beyond pilots to production deployments across diverse functions. PwC predicts blockchain‘s global economic value will exceed $5 trillion by 2030. [6]
With accelerating innovation addressing current challenges, clarity emerging around regulations, and blockchain skills increasingly available, the technology is poised for mainstream adoption.
By delivering transparency, accountability, automation, security and streamlining of complex workflows, blockchain promises to revolutionize both business models and society in the 21st century.